TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDING
Ionic Bonding
– two atoms of opposite charge electrically attracted to one another
Covalent Bonding
– two atoms each sharing electrons within a molecular orbital
Metallic Bonding
– positive metal ions held together in a lattice with a “sea of electrons”
An actual chemical bond is a blend of all three types of bonding. Most often, one type is dominant over others.
METALLIC BONDING

Metal atoms are arranged in a lattice.
Metallic bonding holds lattice together.
– Metallic bonds are much different from ionic or covalent bonds.
– Metal ions have a fixed position within a “sea of electrons”.
Characteristics of Metallic Bonding
1. The orbitals where the valence electrons exist are spread throughout the metal.
– The wave nature of electron extends throughout the whole metal crystal.
2. The energy levels of the orbitals where valence electrons exist are very close together.
3. The excited states of the electrons are very close to the ground states.
– I.e., the gap in energy between the highest ground state electron and the lowest excited state electron is zero.
Consequences of Metallic Bonding
1. Metals are very ductile and malleable because the sea of electrons is flexible.
– If the arrangement of atoms changes, the sea of electrons can rearrange quickly.
2. Metals have high electrical conductivities because the electrons are easily placed in an excited state when they are pushed by an external voltage.
3. Metals have high heat conductivities because the thermal motion can be easily carried by the electrons within an excited state.
COVALENT BONDING
– Atoms that are bonded “share” valence electrons.
– Sharing is what creates covalent bond.
– When atoms bond covalently, new entity termed molecule is formed.
– Nuclei are bound together by their mutual attraction toward the shared electrons.
 Bonding in Diatomic Molecules
Bonding in Diatomic Molecules
Hydrogen
– each atom contributes e– to the bond
– e– in bond belongs to both atoms (e– are shared)
– now each atom has full shell (like He)
– note hydrogen is first exception to octet rule
– Since both atoms share electrons in bond, both atoms have 8 valence electrons, octet rule is satisfied.
IONIC BONDING
– Oppositely charged ions attract each other.
– Metal atoms lose e– and nonmetal atoms gain e–.
– Ions attract each other to form ionic lattice.
Lewis structures can be used to illustrate ionic bonding.
Consider Potassium and Bromine

Consider Calcium and Fluorine
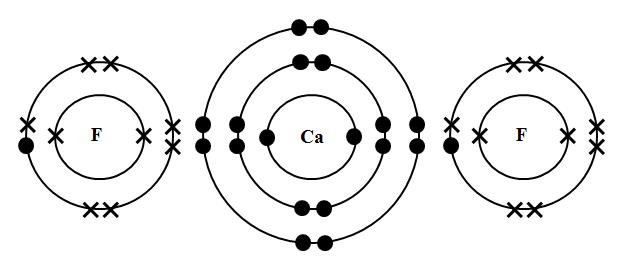
Lewis structures will be much more illuminating when we consider the sharing of electrons (covalent bonding).
Lattice Energy – energy of released when positive and negative ions form crystal lattice due to their attraction for each other.


